
The Cyber Knife provides millimeter precision in the treatment of cancer in any part of the body.
The cyber knife is especially used in complex situations where there are multiple tumors, as well as in the treatment of tumors that cannot be surgically removed.
Reduces potential damage to healthy tissue around the tumor. The cyber knife monitors and locates breathing movements in correlation with the movement of the tumor during the procedure itself, and ensures extremely precise radiation therapy (during the therapy, the patient does not need to hold his breath).
The cyber knife is painless and general anesthesia is not required during the treatment. Patients return to their daily duties very quickly after therapy.
The system enables extremely precise focusing of high doses of radiation to cancerous tissues in the brain and body. At the same time, protection from the effects of radiation on healthy tissue is at the maximum level.
Basically, a cyber knife is an advanced linear accelerator mounted on a robot. It uses beams of radiation aimed at cancerous areas in the brain and body, especially in hard-to-reach places, and delivers high doses of radiation while maximally protecting healthy tissue.
Which conditions are curable:
Primary & metastatic brain tumors
Tumors of the spine
Tumor of the spinal cord
Tumors of soft tissues (lung, kidney, liver, pancreas)
Acoustic neuromas
Meningiomas & skull base tumors
Pituitary tumors
Recurrent & residual tumors
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
Functional disorders, such as trigeminal neuralgia
What are the benefits of a cyber knife?
- Painless therapy
There is no pain associated with radiotherapy delivered via the Radiosurgical Cyber Knife System. - No Frame – The CyberKnife’s ability to correct patient movements during therapy eliminates the pain and discomfort associated with the rigid metal head frame used in other stereotaxic techniques.
- Application to the whole body – The unique design of the cyber knife allows the treatment of tumors or lesions in the whole body, which is a completely new approach in radiosurgery. Radiation therapy can be applied to soft tissues such as the lungs, liver, kidneys and other organs, as well as the brain and spine.
- Outpatient treatment – Cyberknife therapy greatly reduces the risk of complications and long recovery periods that are an integral part of traditional surgery. A cyber knife can perform the so-called “phased” radiosurgery, where the total dose of radiation is divided into at least two and at most five smaller doses over a period of several days. This information is very important in the treatment of larger tumors or those located in sensitive areas, while providing better radiation oncology to the surrounding tissues. After therapy, most patients return home to their daily activities.
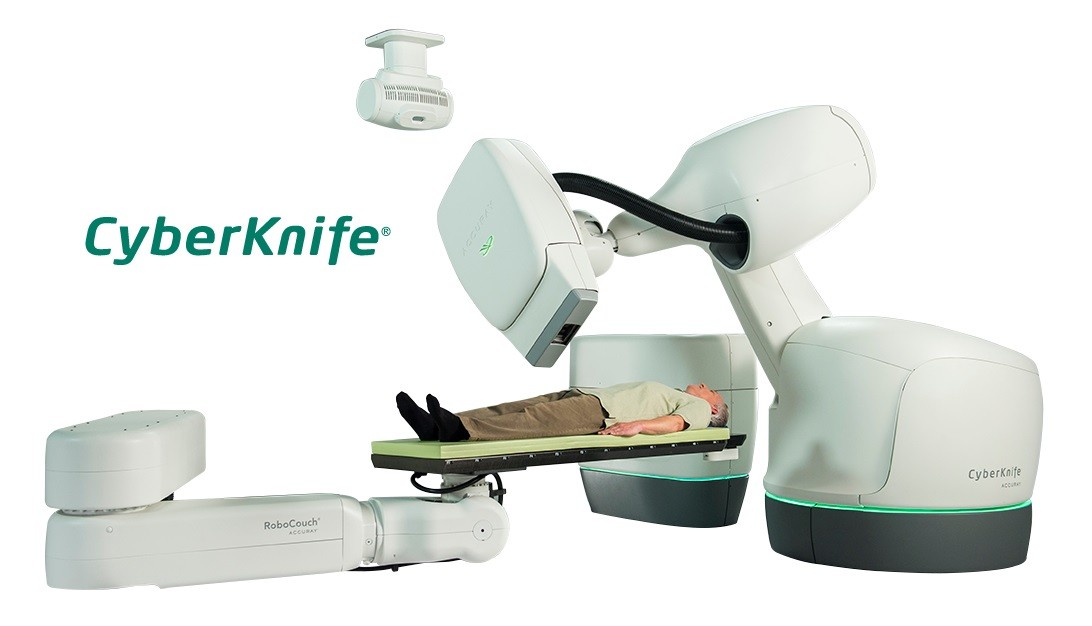
The CyberKnife emits radiation with ten to thirty times greater precision than other linear accelerators. Using a robotic arm, the CyberKnife is able to emit a beam of very thin beams from almost any position, and the irradiated area and the robotic arm are constantly monitored and controlled by a computer. The system can monitor the position of the tumor during irradiation, so it reacts to the slightest movement of the patient so that healthy tissue is not damaged and the radiation is directed only to the tumor.
Thanks to this exceptional precision, it will significantly expand the possibilities in the field of treatment of small tumors near vital structures.

